Memory and storage are essential components of modern computing systems, enabling data retention and fast access to information. As technology advances, various types of memory and storage solutions have emerged, each with its unique characteristics and use cases.
In this blog post, we will delve into the different types of memory vs storage available today, discussing their features, advantages, and common applications.
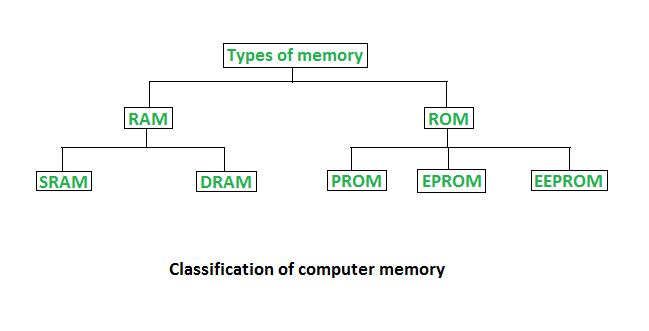
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is a type of volatile memory that provides temporary storage for data that the computer is actively using. It allows for fast read and write operations, making it crucial for running applications and multitasking. Key features of RAM include:
- Speed: RAM provides quick access to data, allowing for rapid retrieval and manipulation.
- Volatility: RAM is volatile memory, meaning it loses its data when power is removed or the computer is turned off.
- Capacity: RAM capacity determines the amount of data that can be stored temporarily. Common RAM capacities range from a few gigabytes (GB) to tens or hundreds of gigabytes.
Applications: RAM is primarily used to store data that is actively being processed by the computer’s CPU. It helps improve system performance by reducing the need for frequent data retrieval from slower storage devices.
2. Read-Only Memory (ROM)
ROM is non-volatile memory that contains firmware or software instructions that are permanently stored and cannot be modified by normal computer operations. Key features of ROM include:
- Non-volatility: ROM retains its data even when power is removed.
- Immunity: ROM is immune to accidental data loss or corruption.
- Limited Modifiability: ROM contents cannot be easily modified or erased, making it suitable for storing critical system instructions.
Applications: ROM is commonly used to store the computer’s firmware or BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), which contains low-level instructions required for booting the system and initializing hardware components.
3. Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
HDDs are traditional mechanical storage devices that use rotating disks (platters) to store data magnetically. Key features of HDDs include:
- Storage Capacity: HDDs provide high storage capacities, ranging from several hundred gigabytes to multiple terabytes (TB).
- Cost-Effectiveness: HDDs are relatively inexpensive compared to other storage options.
- Slower Access Speed: HDDs have slower access times compared to solid-state drives (SSDs) due to mechanical components.
Applications: HDDs are commonly used for bulk data storage, such as storing operating systems, applications, media files, and large datasets.
4. Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
SSDs are storage devices that use flash memory to store data electronically. SSDs have become increasingly popular due to their faster access times and greater reliability compared to HDDs. Key features of SSDs include:
- Speed: SSDs offer faster read and write speeds, resulting in improved system responsiveness.
- Durability: SSDs have no moving parts, making them less susceptible to physical damage and more durable.
- Lower Power Consumption: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Applications: SSDs are widely used in laptops, desktops, servers, and other devices that require fast and reliable storage. They are particularly beneficial for applications that require quick access to data, such as operating systems, databases, and virtual machines.
5. Flash Memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile storage medium that retains data even when power is removed. It is commonly used in USB drives, memory cards, and solid-state storage devices. Key features of flash memory include:
- Portability: Flash memory devices are small, lightweight, and easily portable.
- Durability: Flash memory is resistant to shock, vibration, and extreme temperatures.
- Limited Write Cycles: Flash memory has a finite number of write cycles before it can no longer store new data.
Flash memory is widely used in portable storage devices, digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, and other devices that require compact and reliable storage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Can I upgrade the RAM in my computer?
In most cases, RAM can be upgraded by adding more modules or replacing existing ones. However, it is important to check your computer’s specifications and compatibility before making any upgrades.
What is the difference between RAM and storage?
RAM is temporary memory used by the computer’s CPU for immediate data processing, while storage refers to permanent data storage for long-term retention. RAM provides faster access but has limited capacity, while storage devices offer larger capacities but slower access times.
Can I use SSD and HDD together in my computer?
Yes, many computers utilize a combination of SSDs and HDDs. SSDs can be used for the operating system and frequently accessed data, while HDDs can be used for mass storage of larger files and less frequently accessed data.
Is it possible to recover data from a failed SSD or HDD?
Data recovery from failed storage devices can be challenging and may require specialized services. It is recommended to consult professional data recovery experts to maximize the chances of successful data retrieval.
Can I use flash memory as a permanent storage solution?
While flash memory is non-volatile and can retain data for long periods, it has a limited number of write cycles. Therefore, it is not recommended for continuous and intensive write operations. For long-term storage, SSDs or HDDs are more suitable options.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of memory and storage options available is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to selecting the right solution for your computing needs. From the fast and volatile RAM to the durable and non-volatile flash memory, each type of memory and storage has its strengths and applications.
Consider factors such as speed, capacity, durability, and cost when choosing the appropriate option for your specific requirements. By selecting the right combination of memory and storage technologies, you can optimize the performance, reliability, and efficiency of your computing systems.
